Cancer remains one of the most challenging health issues worldwide, affecting millions of lives each year. Defined as a group of diseases involving uncontrolled cell growth, cancer can strike almost any part of the body, forming a tumor that may be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). When malignant, cancer can spread through a process called metastasis, making early detection and treatment critical. In this article, we explore what cancer is, its symptoms, how oncology experts diagnose and treat it, and the hope offered by modern advancements.
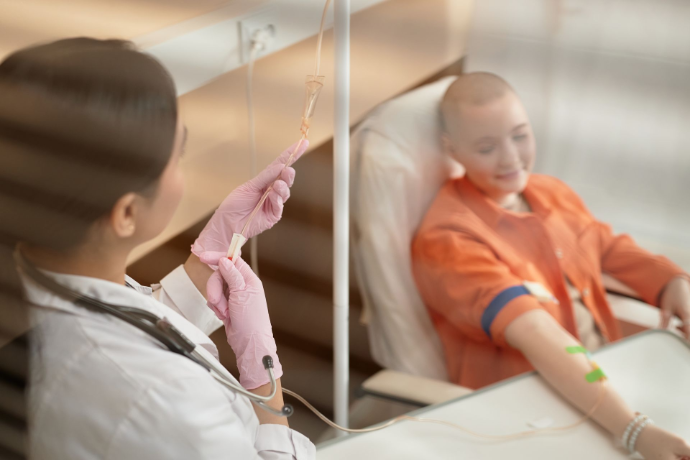
Cancer Treatments : From Chemotherapy to Immunotherapy
Treating cancer has evolved dramatically, thanks to advancements in oncology. Common treatment approaches include :
- Chemotherapy : Uses powerful dru gs to kill fast-growing cancer cells. While effective, it may cause side effects like nausea and hair loss because it can also affect healthy cells.
- Radiation Therapy : High-energy beams target and destroy tumors, often used in combination with other treatments to shrink growths or relieve pain.
- Immunotherapy : A newer treatment option that boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer naturally. It has shown promise in treating melanoma and lung cancer.
- Surgery : Removing localized tumors can lead to remission, particularly if the cancer is caught early.
- Palliative Care : In advanced cases, the focus shifts to improving quality of life through pain relief and symptom management, often in hospice settings.
Each treatment is tailored to the cancer’s type, stage, and the patient’s overall health. Clinical trials also offer access to cutting-edge therapies, providing hope where standard options may fall short.

Living Beyond Cancer : Remission and Survivorship
Achieving remission—when the signs of cancer disappear—is a significant milestone for survivors. However, life after cancer often involves ongoing monitoring for recurrence. Survivors may also face emotional challenges, from fear of relapse to the process of celebrating their resilience. Support groups, counseling, and lifestyle changes—such as quitting smoking or adopting a balanced diet—play a vital role in long-term health and wellness.

The Role of Genetics and Prevention
Some cancers run in families due to inherited mutations, such as the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes linked to breast and ovarian cancer. Genetic testing can identify these risks, allowing for proactive measures like early screening or preventive surgery. In addition, lifestyle choices—like reducing exposure to known carcinogens (e.g., excessive sun exposure or processed meats)—can help lower the risk of developing cancer.

The Future of Cancer Care
The outlook for cancer patients is brighter than ever. Research in immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and personalized medicine is transforming outcomes. Awareness campaigns continue to emphasize early diagnosis, which remains the best defense against metastasis. With every survivor story and scientific breakthrough, we move closer to a world where cancer is no longer a feared word.
- Nutritional Supplements : Carefully selected supplements designed to support immune health and overall vitality.
- Wellness Tools : Products that aid in recovery and help manage stress and fatigue.
- Self-Care Essentials : Items focused on enhancing quality of life during and after treatment.
Our product selection is designed to work alongside medical treatments—not replace them. We encourage patients, caregivers, and survivors to consult with healthcare professionals before starting any new supplement or wellness regimen. Our mission is to provide supportive resources that empower you on your journey toward healing and hope.